ROBOTIC WELDING MACHINE STEEL SCAFFOLDING RINGLOCK PLANKS.
Human vs Robotic Welding
3 min 30 secs, this is the mesurement of our Robot. Time is labour
Solution is 2xRobot Arms and 2xPositioners
Solution is 2xRobot Arms and 2xPositioners

Praparation Table during welding for seamless ongoing fabrication. 4mins per plank
3000mm length, 315mm width
Steel Planks Scaffolding
Repeatedly Test Post Production, measuring accuracy after repetition of movement 0.02mm
Quality Control Q&A
Functional Testing:
Full Range of Motion for Welding Head Movement: To confirm the robotic arm's welding head movement covers the required range, a series of functional tests are conducted. This involves programming the arm to move through its entire range of motion and verifying that it can reach all necessary positions for welding on steel scaffolding planks.
Compatibility Checks for Welding Torch Attachments: Compatibility checks are implemented to ensure seamless attachment of various welding torches and end effectors to the robotic arm. This involves testing different types of torches and end effectors to verify that they can be securely and efficiently connected.
Calibration and Positioning:
Accuracy Verification and Calibration Process: The accuracy of the robotic arm's positioning is verified through precision tests. The calibration process involves aligning and adjusting sensors and encoders to ensure accurate positioning. Regular calibration checks are performed to maintain the precision required for welding on steel scaffolding planks.
Maintenance of Calibration for Weld Precision: Rigorous calibration maintenance is essential to ensure precise weld positioning on steel scaffolding planks. Regular checks and recalibration are performed to account for any deviations that may occur during operation.
Weld Quality and Consistency:
Inspections and Tests for Weld Quality: Specific inspections and tests are implemented to ensure consistent and high-quality weld beads on steel scaffolding planks. This involves visual inspections, non-destructive testing, and possibly destructive testing to verify that the welds meet the required standards.
Verification of Weld Penetration: The robotic arm's ability to achieve the desired weld penetration into the steel material is verified through testing. This may involve X-ray or ultrasonic testing to ensure structural integrity and adherence to penetration specifications.
Speed and Acceleration Testing:
Trajectory Accuracy Validation: Trajectory accuracy is rigorously validated to ensure uniform and efficient welding on each steel scaffolding plank. This testing involves programming the arm to follow predefined trajectories at various speeds and accelerations to verify its performance under different conditions.
Safety Testing:
Integrated Safety Features: The robotic arm and welding system incorporate various safety features to ensure the well-being of both equipment and personnel during welding. These features may include collision detection, emergency stop buttons, and safety barriers.
Emergency Stop Functionality Testing: The emergency stop functionality is tested to ensure its effectiveness in halting the robotic arm and welding process immediately in case of any safety concerns. This involves simulated emergency scenarios to validate the system's responsiveness.
Endurance and Reliability Testing:
Check and Maintenance Plan: A comprehensive check and maintenance plan is established to maximize the lifespan and quality of the entire system. This includes routine inspections, preventive maintenance, and scheduled component replacements to address wear and tear, ensuring the system operates reliably over an extended period.
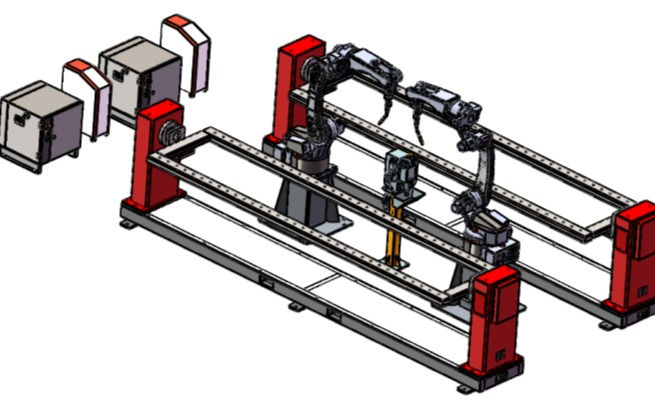
3D model Elevation

3D Plan View of Solution

Front Elevatioin 3D
Remember that while sourcing products from China can be cost-effective, it's essential to do your due diligence to ensure product quality, reliability, and compliance with safety standards. Additionally, be aware of any potential challenges, such as language barriers and cultural differences, and address them proactively in your sourcing process
Connect to our platforms, see below: Signup newsletter: https://www.dracon.co.nz/ LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/timikara-taurerewa/ Our Case Studies: https://www.dracon.co.nz/case-studies Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/timikara_dracon/ Face Book: https://www.facebook.com/DraconNZ/ YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC7LSWZP10pjy4KWUia0xIYA #chinasource #sourcechina #chinaconstruction #buyChina #chinaprocurement #chinaagent #ChinaInspections #chinabuildingmaterials #chinaconstruction #chinarawmaterials #FactoryInspections #chinasteel #asnzs1576 #Chinascaffolding #hydraulicmachine #containerhome #modular #chinashipping
#RoboticWeldingChina #WeldingAutomation #ChinaManufacturing #RoboticsTech #WeldingMachines #AutomationInChina #WeldingSolutions #ChineseManufacturers #RoboticWelders #WeldingIndustry #ChinaEngineering #AdvancedWelding #RoboticPrecision #ChinaAutomation #WeldingInnovation #ManufacturingChina #MetalFabrication #ChineseTechnology #WeldingEquipment #ChinaEngineeringSolutions #WeldingRobots #QualityWelding #ChinaProduction #WeldingProductivity #MadeInChina #RoboticWeldingSolutions #ChinaWeldingExpertise








Comentários